The motors I used for this robot are 2 servomotors modified for speed. You can also use other motors if it's good enough. I didn't have any so I modded 2 servomotors.
Project Description
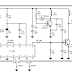
Figure 1 microcontroller-schematic
How to Mod the Servomotors (look at the pictures)
- Remove the four screws from the servo and take it all apart.
- Remove the electronics keeping only the wires from the motor (I kept the other 3 wires from the potentiometer but you don’t have to).
- Try to fit the gears except for one. I glued the big gear to the one beneath it so to be high enough to “get out” of the case. It isn’t exactly a rule for how to do this. Various servos will have various gears so you will need to try until you find the best “combination”.
- Put everything together.
Figure 2 parts
The BODY (look at the picture):
The base of the robot is made of PCB cutted to the properly size.
You will also need 5 screws:
2 for putting together the front and the base of the robot and one for lifting the sensors off the ground (you can use something else here, if you have) 2 for lifting and fixing the microcontroller PCB
Project Files
The base of the robot is made of PCB cutted to the properly size.
You will also need 5 screws:
2 for putting together the front and the base of the robot and one for lifting the sensors off the ground (you can use something else here, if you have) 2 for lifting and fixing the microcontroller PCB
Figure 3 Line-follower
The SENSORS:
I made my sensors using 5 SMD IR emiting diodes, 5 SMD phototransistors and 5 1k SMD resistors. Between the phototransistor and the IR I put some black silicone so the IR light would not come directly to the phototransistor. The PCB design is in the archive “line follower.rar”. It is made in PROTEUS, but I have a word document including all the PCB designs which can be printed on glossy paper or Press and Peel, and then transfered to the PCB using the method of the iron.
The MICROCONTROLLER PCB:
The “heart” of this robot is an ATMEGA8 microcontroller which gets the information from the sensors and drive the L293D motor controller.
Parts list:
1× 28-pin socket (for ATMEGA8)
1× 14-pin socket (for L293)
1x ATMEGA8 – You can also use an ATMEGA 168 or 328. The program is made in Arduino , so if you have an arduino, you can program the microcontroller on it, then remove it from arduino and insert it in this PCB. Also you can program this microcontroller via the 6 pins with an ISP.
1x L293D
1× 16MHz Crystal
2× 22pF (10-28pF)
1x LM7805
1x Push Button
1× 100nF
1× 100uF
1× 4.7 uF
6x LEDs
1× 1K resistor
1× 33R resistor
1x Break Away Header
1x Straight Female Header
1x SwitchWires
Also you will need one 4 AA battery holder.
Everything you need for making the microcontroller pcb and the sensors PCB is in the “line follower.rar” archive. You will find the PCB design, and the schematics which are made in Proteus, but are also available in the Word document.
I made my sensors using 5 SMD IR emiting diodes, 5 SMD phototransistors and 5 1k SMD resistors. Between the phototransistor and the IR I put some black silicone so the IR light would not come directly to the phototransistor. The PCB design is in the archive “line follower.rar”. It is made in PROTEUS, but I have a word document including all the PCB designs which can be printed on glossy paper or Press and Peel, and then transfered to the PCB using the method of the iron.
The MICROCONTROLLER PCB:
The “heart” of this robot is an ATMEGA8 microcontroller which gets the information from the sensors and drive the L293D motor controller.
Parts list:
1× 28-pin socket (for ATMEGA8)
1× 14-pin socket (for L293)
1x ATMEGA8 – You can also use an ATMEGA 168 or 328. The program is made in Arduino , so if you have an arduino, you can program the microcontroller on it, then remove it from arduino and insert it in this PCB. Also you can program this microcontroller via the 6 pins with an ISP.
1x L293D
1× 16MHz Crystal
2× 22pF (10-28pF)
1x LM7805
1x Push Button
1× 100nF
1× 100uF
1× 4.7 uF
6x LEDs
1× 1K resistor
1× 33R resistor
1x Break Away Header
1x Straight Female Header
1x SwitchWires
Also you will need one 4 AA battery holder.
Everything you need for making the microcontroller pcb and the sensors PCB is in the “line follower.rar” archive. You will find the PCB design, and the schematics which are made in Proteus, but are also available in the Word document.
Figure 4 The-electronics
Now all you have to do is take the soldering iron and start to solder all the parts. After you’ve assembled the robot, you need to program the microcontroller. The program is made in Arduino so you can upload it to Arduino and then put the microcontroller in this “motherboard”. You also have the HEX file for an ATMEGA8 using 16Mhz crystal.
Figure 5 Assembly
After everything is done, all you need to do is assemble the robot. You can watch a video of me assembling it. Enjoy!
Project Files
| File Name | File Size |
|---|---|
| code file | 2.98 KB |
| code file in hex format | 2.98 KB |
| how to place component text file | 48 KB |
| how to construct the robot is provided in this file everything step wise | 556 KB |
| microcontroller.DSN | 58.62 KB |
| layout | 36.72 KB |
| pcb printing format | 34 KB |
| sensor | 60.39 KB |
| sensor layout | 19.66 KB |
source : http://www.eeweb.com/project/rinkesh_kurkure/line-follower1
 15:00
15:00
 Unknown
Unknown






 Posted in:
Posted in: 




2 comments:
I would like to say that this blog really convinced me, you give me best information! Thanks, very good post.printed circuit board manufacturers
what can be used in place smd ir transitor ,smd photodiode ,smd resistor 1k ?
Post a Comment